
Adolescent cannabis use is associated with increased cannabis misuse as an adult, issues with memory and concentration, long-term cognitive complications, and poor psychiatric outcomes including social anxiety, suicidality and addiction. Adolescent cannabis users are therefore particularly vulnerable to the potential adverse effects of cannabis use. The endocannabinoid system is directly involved in adolescent brain development. High risk groupsĪ number of groups have been identified as being at greater risk of developing cannabis dependence and, in Australia, for example, have been found to include adolescent populations, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders and people suffering from mental health conditions. The researchers concluded there is emerging evidence that positive experiences to early cannabis use are a significant predictor of late dependence and that genetic predisposition plays a role in the development of problematic use. The main factors in Australia, for example, related to a heightened risk for developing problems with cannabis use include frequent use at a young age personal maladjustment emotional distress poor parenting school drop-out affiliation with drug-using peers moving away from home at an early age daily cigarette smoking and ready access to cannabis. Increasing evidence is being shown for the elevation of associated problems by the frequency and age at which cannabis is used, with young and frequent users being at most risk. Risk factorsĬertain factors are considered to heighten the risk of developing cannabis dependence and longitudinal studies over a number of years have enabled researchers to track aspects of social and psychological development concurrently with cannabis use. It can also be caused by being prone to becoming addicted to substances, which can either be genetically or environmentally acquired.
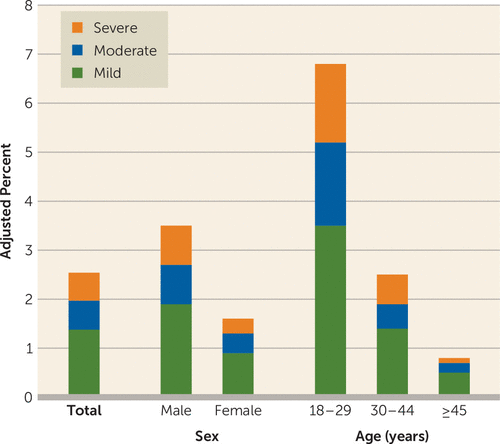
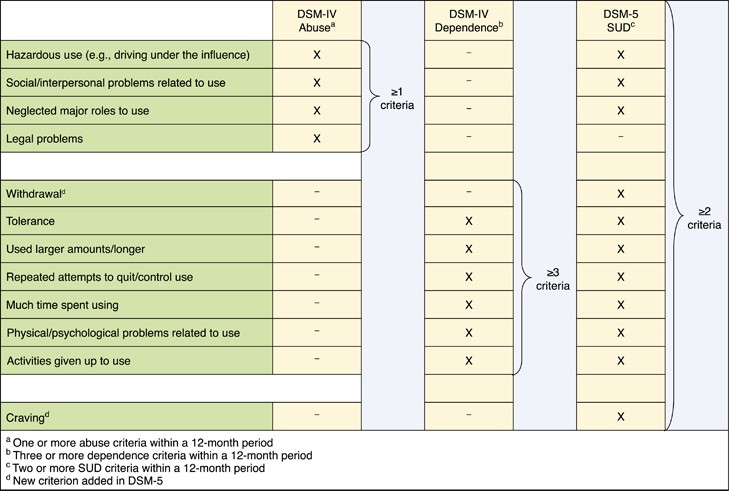
Increasing the strength of the cannabis taken and an increasing use of more effective methods of delivery often increase the progression of cannabis dependency. CauseĬannabis addiction is often due to prolonged and increasing use of the drug. About 12% of heavy cannabis users showed cannabis withdrawal as defined by the DSM-5, and this was associated with significant disability as well as mood, anxiety and personality disorders. Most symptoms begin during the first week of abstinence and resolve after a few weeks. It is often paired with rhythmic movement disorder. Symptoms may include dysphoria (anxiety, irritability, depression, restlessness), disturbed sleep, gastrointestinal symptoms, and decreased appetite. WithdrawalĬannabis withdrawal symptoms occur in one-half of people in treatment for cannabis use disorders. Of those who use cannabis daily, 10–20% develop dependence. Ĭannabis dependence develops in about 9% of users, significantly less than that of heroin, cocaine, alcohol, and prescribed anxiolytics, but slightly higher than that for psilocybin, mescaline, or LSD. One study has shown that between 2001–20–2013, the use of marijuana in the US doubled. The mechanisms that create this tolerance to THC are thought to involve changes in cannabinoid receptor function. Tolerance to the behavioral and psychological effects of THC has been demonstrated in adolescent humans and animals. Ĭannabis users can develop tolerance to the effects of THC.

Ĭannabis users have shown decreased reactivity to dopamine, suggesting a possible link to a dampening of the reward system of the brain and an increase in negative emotion and addiction severity. These changes require the user to consume higher doses of the drug to achieve a common desirable effect (known as a higher tolerance), reinforcing the body's metabolic systems for eliminating the drug more efficiently and further down-regulating cannabinoid receptors in the brain. Prolonged cannabis use produces both pharmacokinetic changes (how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted) and pharmacodynamic changes (how the drug interacts with target cells) to the body. The sedating and anxiolytic properties of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in some users might make the use of cannabis an attempt to self-medicate personality or psychiatric disorders. īased on annual survey data, some high school seniors who report smoking daily (nearly 7%, according to one study) may function at a lower rate in school than students that do not.

Psychiatric comorbidities are often present in dependent cannabis users including a range of personality disorders. Reduced blood flow in prefrontal cortex of cannabis users.Ĭannabis use is associated with comorbid mental health problems, such as mood and anxiety disorders, and discontinuing cannabis use is difficult for some users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
